Predicting Phase Equilibria for Sulfolane-Supported Selective Sour-Gas Absorption
- Research Highlights
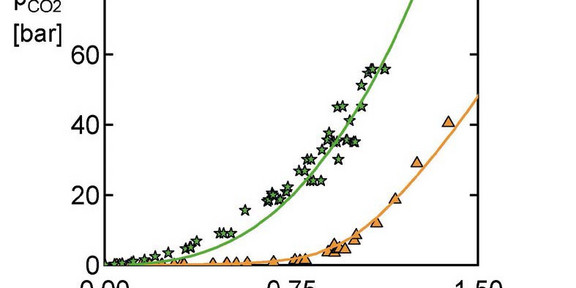
In the chemical industry, aqueous amine solutions are widely used in sour-gas absorbers to reduce the emission of climate
wrecking gases like CO2. The effectivity of these amine solutions is enhanced by adding physical solvents. Predicting the
absorption is challenging, involving multicomponent electrolyte systems, mutually affecting phase and reaction equilibria
at wide temperature and pressure range. The thermodynamic model ePC-SAFT was used here to predict the selective
absorption of CO2 over H2S (and vice versa) in an ultimately complex solution. The absorption depends on loadings of the
sour gases and on the composition of the aqueous solution, which contains a chemical solvent (methyl diethanol amine
(MDEA)) and a physical solvent (sulfolane).