Modeling the CO2 Solubility in Electrolyte Solutions with ePC-SAFT
in
- Research Highlights
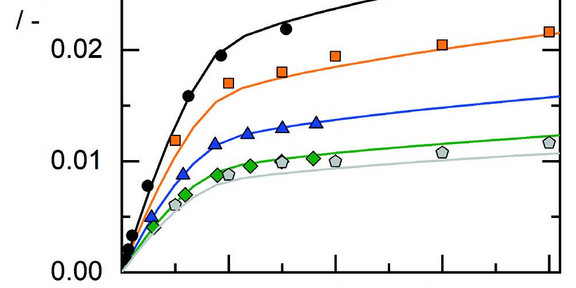
CO2 solubility is predicted as function of pressure, temperature and salt concentration
Carbon dioxide (CO2) solubility in aqueous electrolyte solutions is of special interest for carbon capture and storage or
utilization, particularly as function of temperature, pressure, and electrolyte concentration. Unfortunately, experimental
determination at such multivariable conditions is laborious. Therefore, the ion-based model ePC-SAFT was used to model
the CO2 solubility in such systems in a broad range of conditions. The CO2 solubility was successfully modeled in water and
in aqueous electrolyte solutions containing alkali and earth alkali chlorides and nitrates or mixtures thereof.